Introduction of Phosphorus and Derivatives Market
Phosphorus and phosphoric acid are inorganic compounds that play crucial roles in various industrial and chemical processes. Phosphoric acid, in its crystalline form, is typically characterized by its mild acidity, appearing weak in nature. It is colorless, odorless, and possesses good solubility in water, making it a versatile chemical for a wide range of applications. However, despite its seemingly benign properties, it should be handled with caution, as it is corrosive to ferrous metals and alloys, which can lead to degradation over time.
One notable property of phosphoric acid is its susceptibility to decomposition at high temperatures, which should be taken into account when considering its use in various processes. Moreover, when phosphoric acid is combined with alcohol, it has the potential to produce toxic fumes, highlighting the importance of careful handling and storage.
One of the most well-known applications of phosphoric acid is in the food and beverage industry, particularly in soft drinks. It serves a dual purpose in these beverages: imparting a tangy flavor that is characteristic of many sodas and acting as a preservative. The acidity of phosphoric acid not only contributes to the distinctive taste of soft drinks but also helps prevent the growth of mold and bacteria, which can thrive in sugary solutions. Therefore, it plays a crucial role in maintaining the quality and safety of these beverages.
Definition
White and red phosphorus are the two allotropic forms of phosphorus, a flammable nonmetallic element. These phosphorus derivatives include phosphoric acid, phosphorus acid, phosphorus oxychloride, phosphorus pentachloride, phosphorus tribromide, sodium hypophosphite, tributyl phosphate, and triethyl phosphate. The crystalline acid phosphoric acid, a phosphorus derivative, is typically weak, colourless, and odourless. These inorganic substances have excellent solubility in water and are corrosive to ferrous metal and alloys. High temperatures tend to cause them to break down. When these are mixed with alcohol, hazardous vapours may be produced. It imparts a tart flavour to soft drinks and stops mould and germs from growing, which may flourish readily in a sweet solution. Phosphoric acid also contributes significantly to the soda’s acidity.
Key basics of phosphorus and derivatives market
- Due of its physical characteristics, diammonium phosphate (DAP) is the most widely used phosphatic fertiliser. DAP has an N-18% and P2O5-46% composition. DAP fertilisers are ideal for any agricultural crop to offer beginning doses of nitrogen and low sulphur together with full phosphorus nutrition throughout crop growth and development. It may be used for tilling in the autumn and for sowing and pre-sowing cultivation in the spring. By temporarily raising the pH of the soil solution surrounding the fertiliser granules through soil dissolution, fertilisers on acidic soils can more effectively bind phosphorus. Sulphur in fertiliser also helps plants absorb nitrogen and phosphorus more effectively.
- The majority of medicinal uses for phosphoric acid include dental cement, the production of albumin derivatives, urine acidification, the removal of necrotic (dead cells or tissue) detritus, anti-nausea medications, teeth whiteners, and mouthwash.
- When used for teeth whitening, phosphoric acid can change the surface of the teeth. Following bleaching, using 37% phosphoric acid can considerably increase the acid’s decalcifying impact on the enamel surface, resulting in an unevenly scratched surface. Additionally, it may cause tooth sensitivity.
Restraint in phosphorus and derivatives market
- Environmental Concerns: Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plant growth and is widely used in fertilizers to enhance crop yields. However, the excessive use and mismanagement of phosphorus-based fertilizers can lead to adverse environmental consequences. When runoff from agricultural fields containing phosphorus reaches water bodies, it can contribute to nutrient pollution, causing issues such as harmful algal blooms and eutrophication. These phenomena can harm aquatic ecosystems, disrupt water quality, and even lead to the death of aquatic life.
- Resource Depletion: Phosphorus is a finite resource, and its extraction relies on mining phosphate rock, which is a non-renewable process. As the demand for phosphorus in agriculture and other industries continues to grow, concerns arise about the long-term sustainability of phosphorus reserves. If not managed sustainably, the depletion of these resources can lead to supply shortages and price volatility in the phosphorus and derivatives market.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: In response to environmental concerns, regulatory bodies in various regions are imposing stricter regulations on phosphorus use and management. These regulations may include limits on the phosphorus content in fertilizers, runoff mitigation requirements, and reporting obligations for industries that use phosphorus-based chemicals. Compliance with these regulations can pose challenges for businesses operating in the phosphorus and derivatives market and may require investments in new technologies and practices.
- Alternative Technologies: The development of alternative technologies and practices for nutrient management, such as precision agriculture, bio-based fertilizers, and phosphorus recycling, poses a potential restraint for traditional phosphorus and derivatives manufacturers. As sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives gain traction, there may be a shift in demand away from conventional phosphorus-based products.
- Consumer Awareness: Growing consumer awareness of environmental issues and sustainable agriculture practices can influence purchasing decisions. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that are produced with minimal environmental impact. This shift in consumer preferences can put pressure on manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices in the phosphorus and derivatives market.
For more about market visit
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-phosphorus-and-derivatives-market
Growth rate in phosphorus and derivatives market
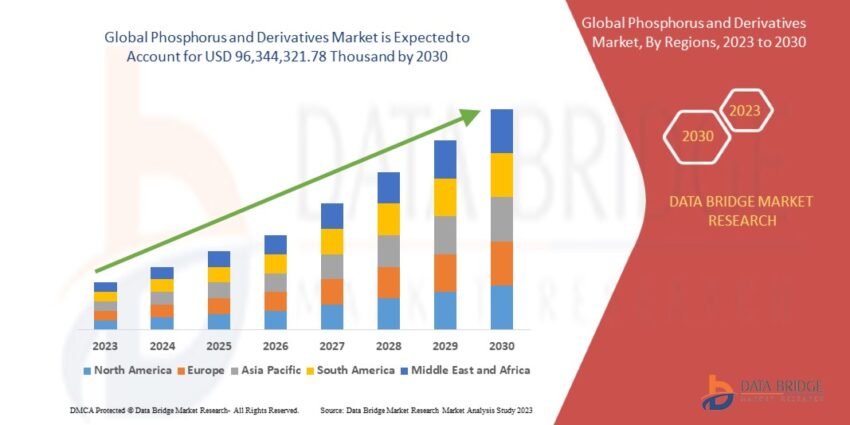
- Data Bridge Market Research’s comprehensive analysis reveals a promising outlook for the global phosphorus and derivatives market. Over the forecast period spanning from the present to 2030, this market is anticipated to exhibit robust growth, with a commendable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.14%. By the year 2030, the market is expected to attain a substantial valuation of USD 96,344,321.78 thousand.
- Among the various segments within the phosphorus and derivatives market, phosphoric acid stands out as the largest product segment. This prominence is attributed to the increasing utilization of phosphorus in this market. Phosphoric acid, a crucial component within the phosphorus and derivatives sector, finds widespread application across diverse industries, including agriculture, food and beverage, and chemical manufacturing.
- The significance of phosphoric acid can be attributed to its multifaceted properties and versatility. It is a key ingredient in the production of fertilizers, playing a pivotal role in enhancing crop yields and ensuring global food security. Additionally, phosphoric acid is an essential component in the food and beverage industry, where it is utilized for its acidity and as a flavoring agent in various products.
- Phosphoric acid is a fundamental building block in the chemical industry, contributing to the synthesis of a wide range of chemicals and compounds. Its versatility extends to water treatment processes, where it is employed to regulate pH levels and remove impurities.